If you are looking for a safe and healthy recovery after getting an orthopaedic surgery such as knee replacement or even a fracture, then you must also be factoring in good nutrition along with ensuring plenty of rest and adequate wound treatment. An orthopedic surgery will bring tremendous stress on the body as it elevates the metabolism of the body while it is in the mode of repair.
A well-balanced and nutritious diet becomes important for proper development, repair and rapid recovery of the tissue. The nutrients listed below are the ones that serve as building blocks during the postoperative period and help to recover quickly and healthily. Most of these nutrients are readily obtainable from foods we eat daily. Let ‘s dive in to find out about these bone-healing foods that can help you recover more quickly.
1. Protein
Protein makes up 55% of our bone volume and therefore becomes a main component in bone-healing diet. Adding this essential nutrient to the diet after an orthopedic operation has been shown to minimize bone loss, decrease the risk of post-surgical infections and increase bone mass.
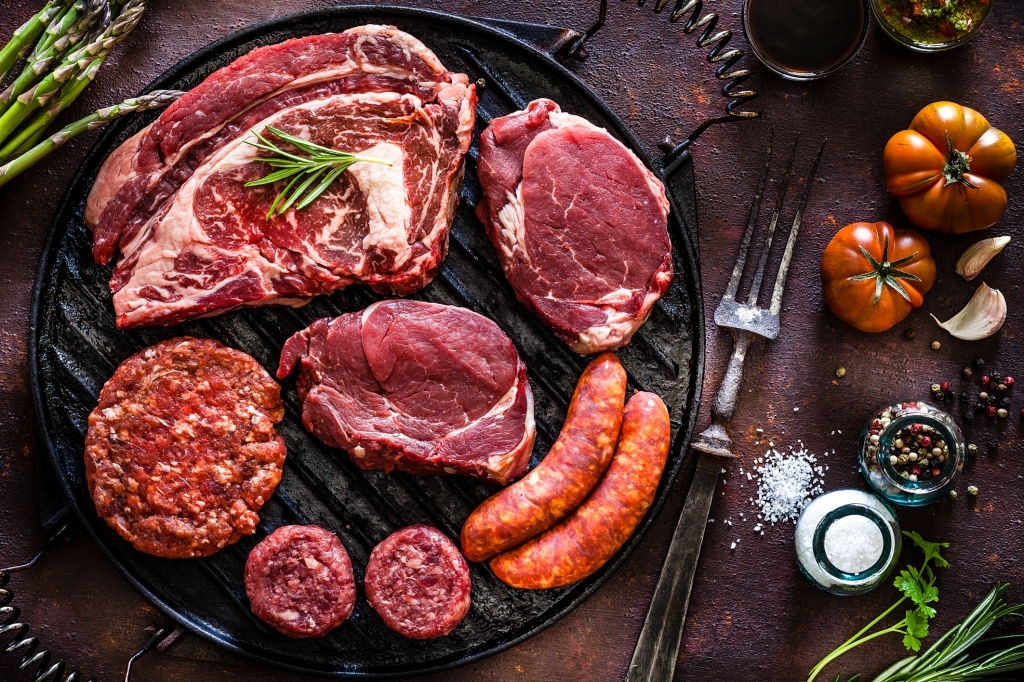

To obtain the essential amino acids present in protein, it is suggested that the following food items shall be included in their diet:
- Soybean and soy products
- Quinoa
- Chia seeds
- Spinach
- Beans
- Artichokes
- Peas
- Lentils
- Meat
- Poultry
- Seafood
- Egg
2. Calcium
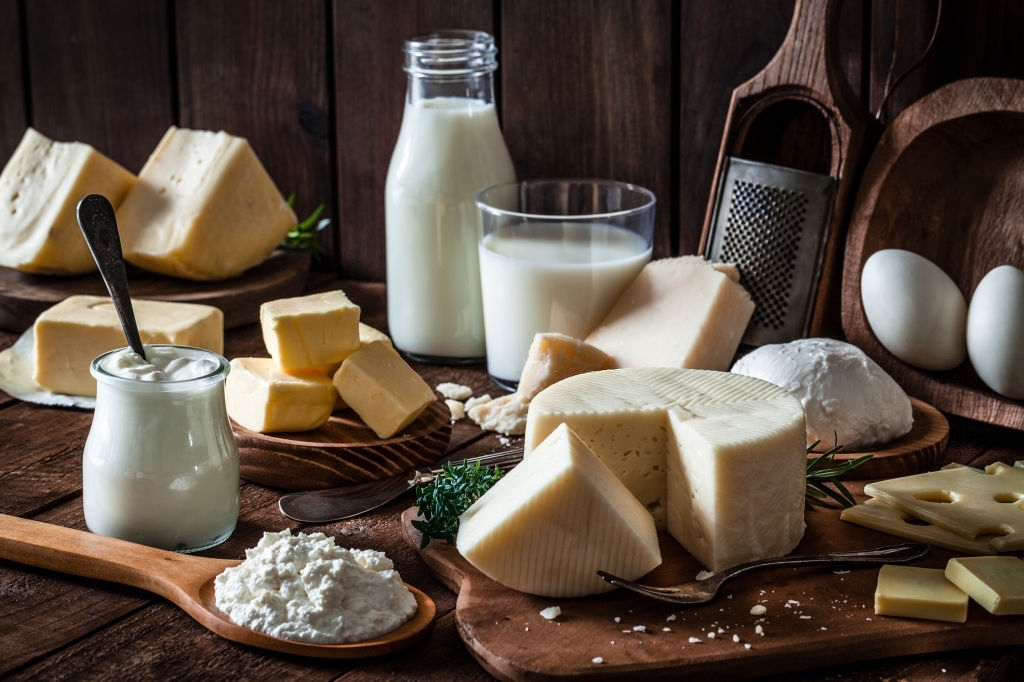

Calcium serves in bone formation along with protein, and is therefore an important post-surgery mineral. In order to function properly, even our heart, muscles and nerves need calcium. The best calcium sources include dairy products such as low-fat and no-fat milk, yogurt and cheese; fortified foods such as beans, tofu or rice milk, for example. Dark leafy vegetables such as broccoli, kale and spinach, and more. Studies also suggest a realistic target for bone health is 600-1,000 milligrams of calcium per day.
3. Vitamin D

Vitamin D acts with Calcium to support bone health as it improves the absorption and use of calcium in our body. Sun is the best source of vitamin D however, the capacity of our body to produce vitamin D depends on the time of year, the time of day, and where we live. It is also possible to receive a limited amount of Vitamin D from food sources such as fatty fish, salmon , tuna, egg, cheese, or fortified milk.
4. Vitamin C

Vitamin C has antioxidant properties, and is therefore an essential part of the immune function of our body , particularly if it is healing. It can neutralize the influence of disease-promoting, free radicals. Vitamin C also assists in the synthesis of collagen, which is needed to repair tendons, ligaments and other surgical wounds.
A good source of vitamin C is citrus fruits such as orange, strawberries, kiwi, and lemon; and vegetables such as broccoli, bell peppers, sprouts, and more. During the postoperative phase, the regular prescribed Vitamin C intake is 500 mg, as the body needs more of this vitamin for better healing.
5. Zinc

After an orthopaedic surgery, zinc along with vitamin C and protein will significantly improve the recovery. Deficiency of the same is related to poor bone health.
Due to its function in collagen synthesis, zinc has been shown to help wound healing, unite bone fractures and prevent osteoporosis. This mineral is used mainly in animal feed. The best non-vegetarian sources of protein are oysters, beef, dark poultry etc. Fortified cereals, wheat, beans, nuts, on the other hand, often have small amounts of zinc.
Adding the above bone healthy nutrient-related foods into your diet will also help you recover from surgery quickly. But be sure to consult your orthopaedic surgeon for the correct proportion of each nutrient in your diet.